The widespread use of cryptocurrency in the United States has extended beyond the internet and banking sectors and has affected more conventional businesses, like food, in recent years.
From farm to fork, blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies are affecting how companies run, how consumers pay, and how supply chains are controlled.
Though still not common, digital currencies are becoming present in the food industry, where they are altering the relationship between businesses and consumers.
Simplified Payments and Reduced Transaction Fees
The capacity to take digital currencies as payment is one of the most obvious and immediate consequences of cryptocurrency use in the U.S. food sector. Many supermarkets, cafes, food trucks, restaurants, and even some grocery stores now let clients pay with cryptocurrency.
Especially for small or independent enterprises, this innovative means of payment has advantages such as reduced transaction costs when compared to conventional credit card systems.
Avoiding large processing costs can significantly help businesses that depend on tiny margins, including local eateries or specialty coffee shops. Payments made in cryptocurrency are often quicker and occasionally more secure, therefore lowering the possibility of fraud or chargebacks.
This attracts both companies and consumers, particularly in cities with tech-savvy people, as evidenced by the number of interested parties on the current BTC to USD exchange rate.
Adoption Patterns and Transaction Data in U.S. Food Businesses
- Crypto-accepting restaurants in the U.S. exceeded 2,300 by the end of 2024, based on industry data aggregated by CoinMap and Yelp Business Listings. This number reflects a 45 percent increase compared to two years prior.
- Transaction fees on crypto payments range between 0.5 to 1 percent, compared to 2 to 4 percent for credit card networks like Visa or Mastercard.
- According to a BitPay report, food and beverage spending made up 9.3 percent of all crypto transactions on their platform during Q3 of 2024, marking the third largest spending category after retail goods and travel.
- Cities leading in crypto food payments include San Francisco, Austin, and Miami, each with concentrated consumer adoption and blockchain business ecosystems.
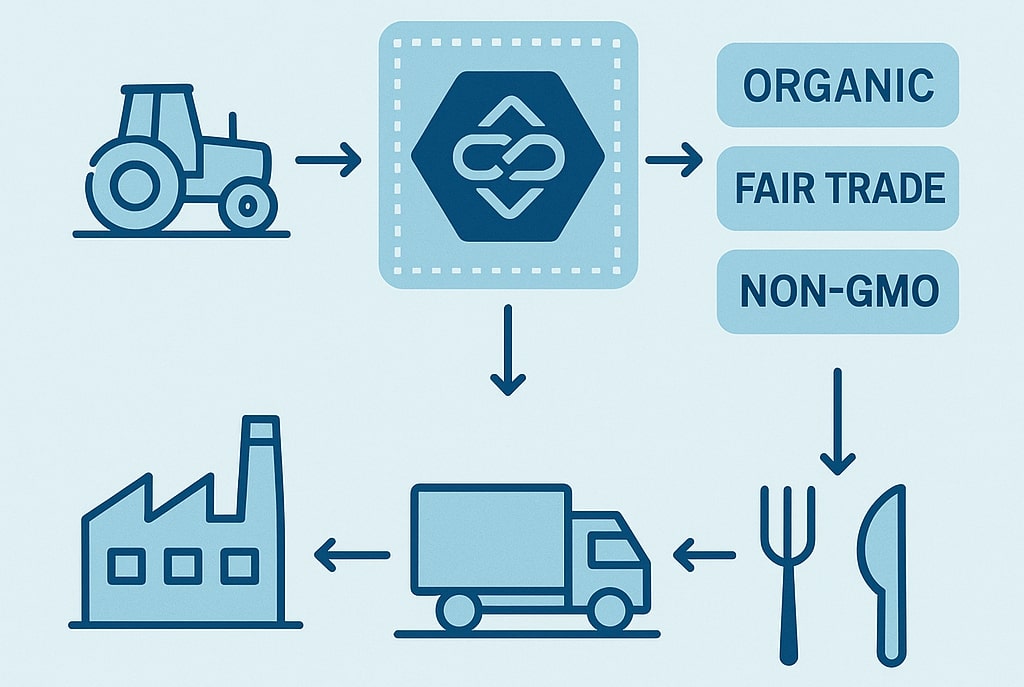
How Blockchain Technology Could Reinforce Food Chain Trust and Accountability
Often running on blockchain technology, cryptocurrency is helping to increase food supply chain transparency. Using blockchain ledgers, retailers, wholesalers, and food manufacturers may monitor items from their point of origin to the customer’s plate. A decentralized and unchangeable system can record every stage of the supply chain.
Particularly in situations with food safety recalls or sustainability assertions, this tracking is quite beneficial. Blockchain, for instance, can assist in confirming whether a product marked “organic” really satisfies the required criteria or whether fish was sustainably caught.
This openness strengthens consumer confidence, and it motivates ethical behavior among manufacturers and merchants.
A food brand can present a QR code to shoppers that links to blockchain data showing when, where, and how the item was produced. This changes how people view claims like non-GMO, fair-trade, or pesticide-free.
Example
Walmart adopted blockchain traceability across its leafy greens supply by partnering with IBM Food Trust. The system reduced traceback time during food safety checks from 7 days to 2.2 seconds.
Nestlé, Tyson Foods, and Dole joined the IBM Food Trust platform for supply tracking, contributing to over 18 million tracked food products by mid-2024.
Encouraging Local and Independent Producers
For farmers with no access to conventional banking systems and small-scale food producers, cryptocurrency has also been a great enabler. Local farmers can sell straight to companies or people using crypto wallets and blockchain-enabled payment systems, bypassing middleman financial institutions.
This has been especially helpful at online platforms linking consumers with growers, organic co-ops, and farmers’ markets.
Furthermore, the inexpensive character of cryptocurrency transactions can promote peer-to-peer commerce, hence enabling smaller enterprises to compete with big agribusinesses.
It also allows companies in underprivileged or rural areas to join the larger economy by avoiding the usually high costs and bureaucracy connected with traditional payment systems.
Tools Supporting Farmers Without Banks
Platforms like AgUnity and FarmShare now give American farmers access to direct digital payments without any need for banks. A grower in rural Kentucky can sell fresh produce straight to a restaurant in Ohio using a crypto wallet on a basic smartphone.
No middleman, no delays, no paperwork. Just direct access to funds and a new level of control over each transaction.
Improved Consumer Interaction with Loyalty and Incentives
Certain eateries have included Bitcoin in their loyalty schemes. Rather than conventional points or discounts, they provide token-based incentives that may be valued or exchanged. Customer retention tactics under this new paradigm include investment and creativity.
As tokens can usually be used across several companies inside a network or even traded for other digital assets, these blockchain-based loyalty programs also provide consumers more freedom. For restaurants and food brands, this notably appeals to younger generations who are more acquainted with digital currency.
Blockchain Loyalty in Action: How Restaurants Use Tokens
View this post on Instagram
Burger King partnered with Robinhood to offer Bitcoin rewards through its Royal Perks program, allowing customers to earn crypto instead of standard points. Other chains like Starbucks have explored tokenized rewards through blockchain pilot programs that let users track and redeem benefits across digital platforms.
Legal Uncertainty and Volatility Slow Business Adoption
Most food businesses avoid crypto payments not because of technology gaps but because of unclear IRS treatment and inconsistent state-level guidance.
A small café accepting Bitcoin in California must report it differently than a bakery in Texas. In 2024, at least eight states proposed bills related to crypto taxation, none with uniform outcomes.
Without federal alignment, even basic bookkeeping becomes risky. Add the daily value swings of coins like Ethereum, and owners face real financial exposure. Until compliance standards are settled, adoption will stay cautious.
Tech-Friendly Branding and Marketing Edge
Companies that embrace bitcoin sometimes brand it as a benefit. Being crypto-friendly can indicate creativity and forward-thinking, which is especially appealing to Gen Z and millennial consumers. It frames food brands and restaurants as components of a contemporary, digital-first economy.
Some food brands have gone even further with limited-time menu items only available with cryptocurrency or by organizing events honoring blockchain culture. These marketing strategies not only draw techies but also create media attention and customer interest.
Key Elements of a Successful Crypto-Friendly Food Brand
- Clear signage or website badges showing crypto payment acceptance
- Menu items or deals available exclusively through digital currency
- Token-based loyalty rewards integrated into mobile apps
- Partnerships with blockchain platforms or NFT creators for promotions
- Social campaigns targeting Gen Z with crypto giveaways or challenges
- Consistent messaging that connects food with digital innovation
Food Security Projects and Donations
Food-related charity is also using cryptocurrency. To support operations or particular hunger-relief initiatives, certain charitable organizations and food banks have begun accepting crypto donations.
The transparent nature of blockchain technology means that contributors can trace how funds are used, strengthening trust in philanthropic activities.
Furthermore, smart contracts built on blockchain can assist underprivileged areas with food delivery. Particularly in times of crisis, these digital contracts can efficiently control resource allocation or automate food delivery logistics.
Binance Charity’s Crypto Food Vouchers in Uganda
Binance Charity launched a blockchain-based voucher system in Uganda that allowed underprivileged families to receive food and school supplies through QR-code-based crypto vouchers.
Local vendors scanned the codes to provide goods, and every transaction was recorded transparently on the blockchain, ensuring full traceability of donations.
EatBCH Delivers Meals via Bitcoin Cash in Venezuela and South Sudan
Thank you #BCH 💚🙏 pic.twitter.com/cP2WkxEHPN
— eatBCH Venezuela (@eatBCH_VE) November 9, 2022
EatBCH, a volunteer-run initiative, uses Bitcoin Cash donations to buy and distribute meals directly to people facing hunger in Venezuela and South Sudan. The simplicity of mobile wallets allows the team to bypass banks, buy local ingredients, and deliver food almost instantly, even in regions with unstable infrastructure.
The Giving Block Supports U.S. Food Charities With Crypto Donations
The Giving Block has enabled several U.S.-based food banks and hunger-relief nonprofits to accept cryptocurrency, including Feeding America affiliates.
Donors can choose coins like Ethereum or Bitcoin, and receive tax-deductible receipts. Food charities benefit from fast, secure donations and greater visibility in the crypto community.
Conclusion
Though still in its early stages, cryptocurrency use in the U.S. food sector is starting to show clear benefits. Digital currencies are changing the way food companies run, from empowering small producers and increasing consumer involvement to streamlining payments and boosting supply chain transparency.
Although issues such as volatility and regulation still exist, the possibility for invention is great.
Not only in how we pay for our meals but also in how food is produced, sold, and delivered, as the U.S. food industry modernizes, cryptocurrency and blockchain technology are probably going to play a bigger role. This digital evolution offers fresh chances for forward-looking companies and consumers to engage with food in more intelligent, linked ways.